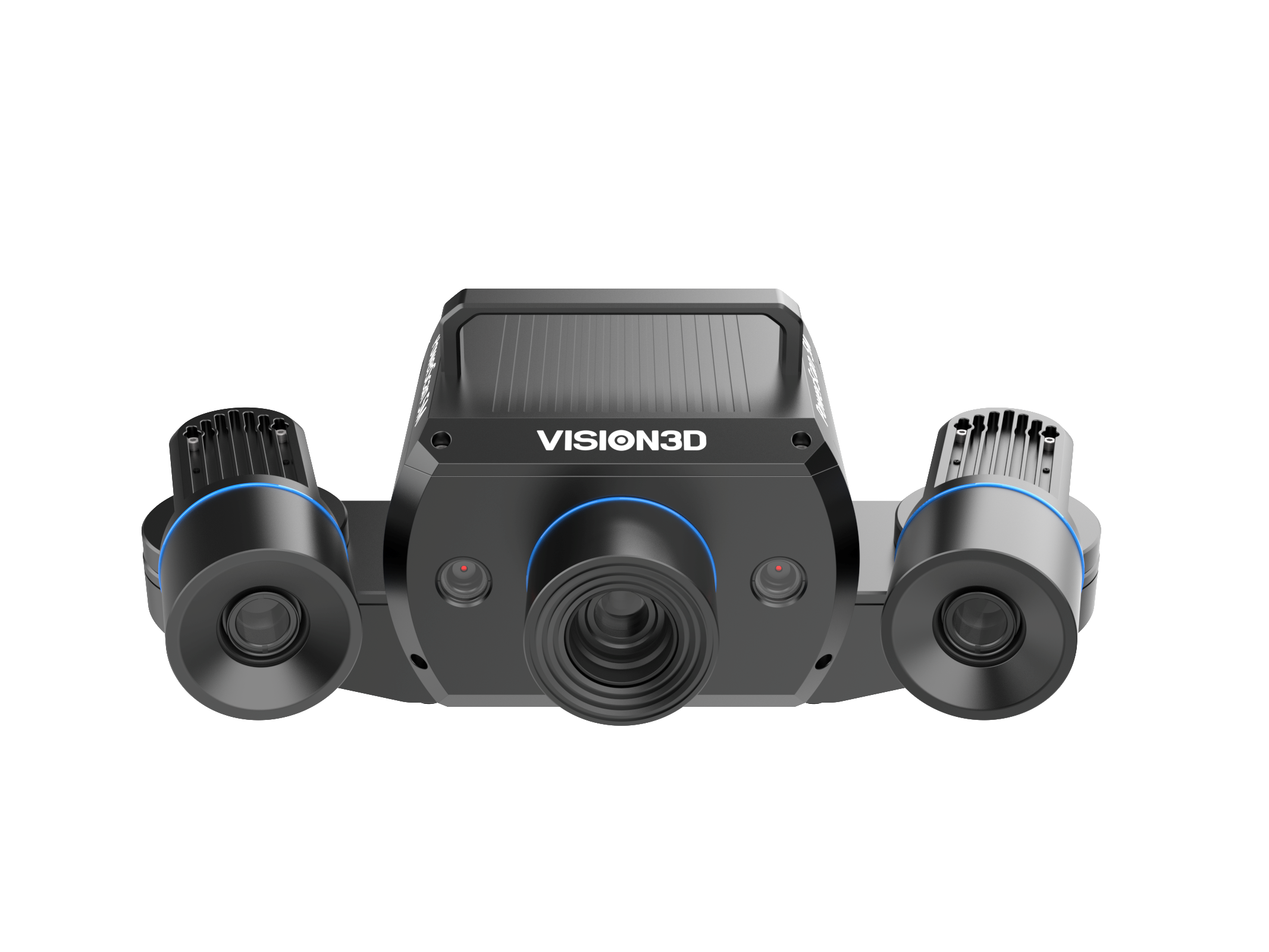
Precision Inspection of Gas Turbine Engine Blades
In the aviation industry, gas turbine engines are the most widely utilized powerplants. Consequently, aerospace manufacturers impose extremely stringent quality inspection standards for engines and their critical components.
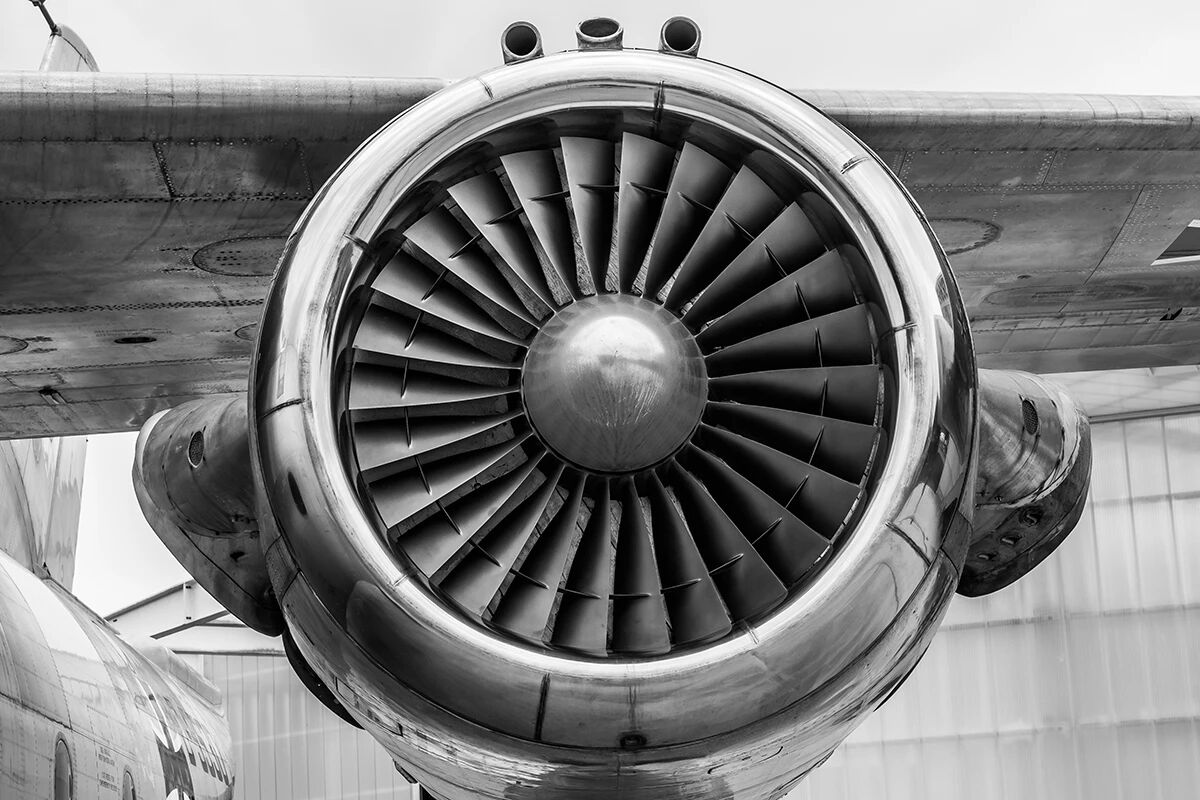

The aerodynamic performance of turbine blades directly determines the energy conversion efficiency of the engine. Therefore, defect detection in turbine blades plays a vital role in ensuring aircraft safety and preventing catastrophic failures.
Project Background
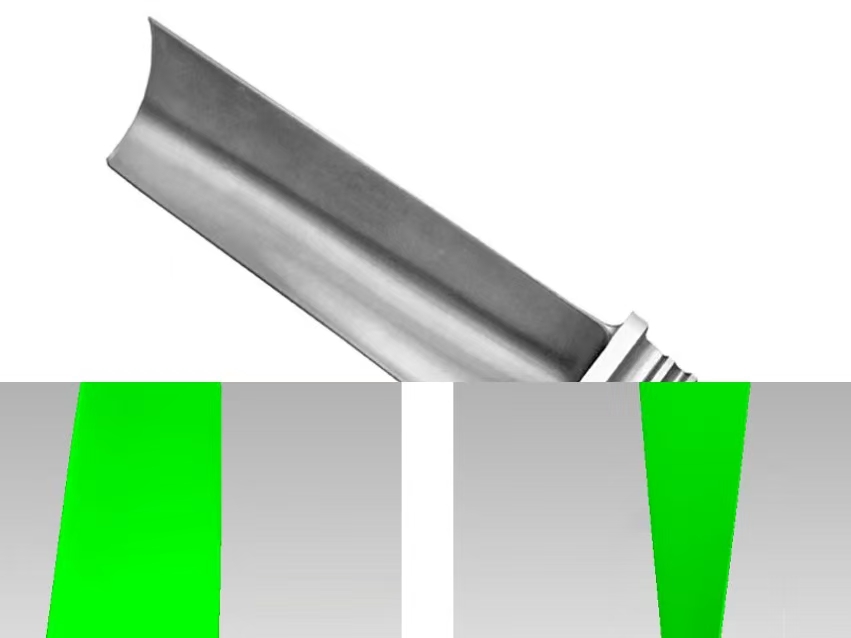
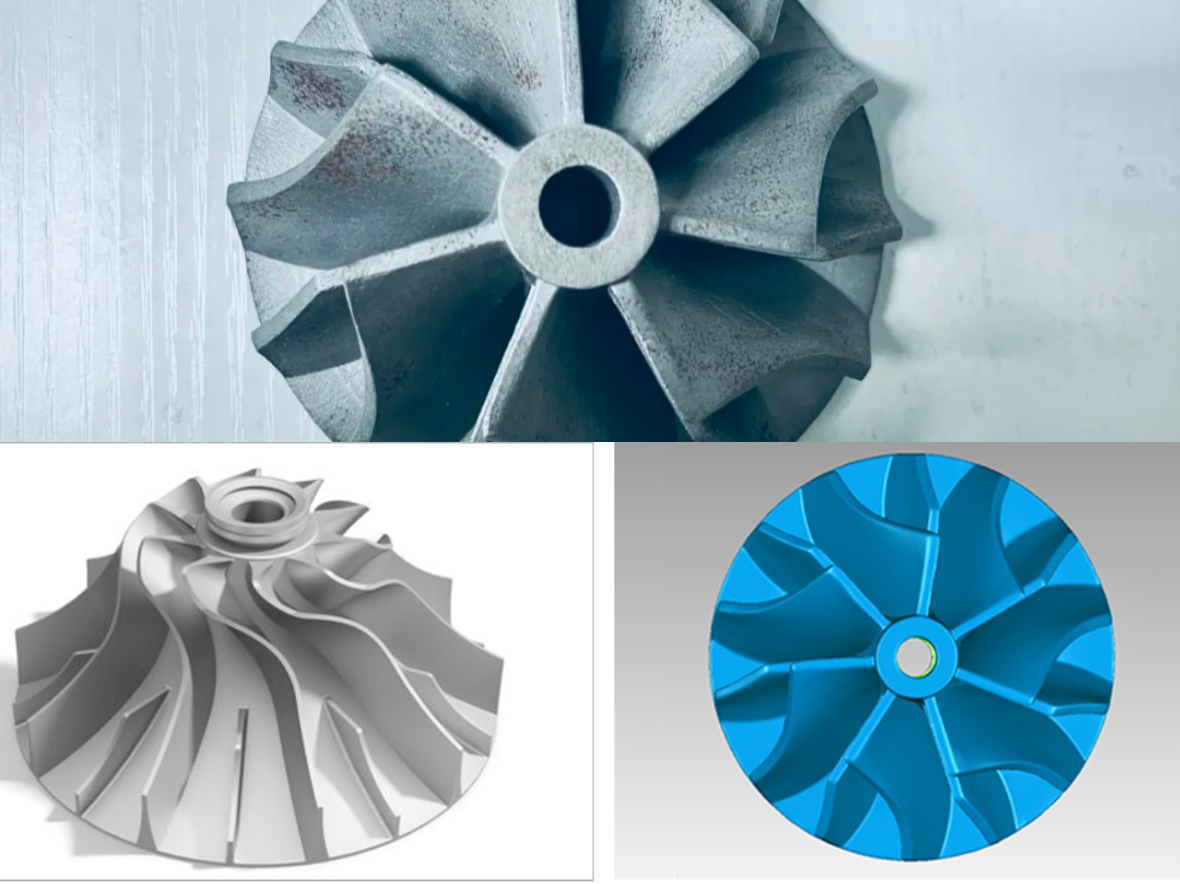
Turbine blades are produced via investment casting (precision casting) in multi-vane segments. The blade structure is highly complex, featuring spatial curved surfaces on both the leading and trailing edges. With narrow measurement spaces and dual-inclined side-surface structures, the blades demand a highly adaptable inspection methodology.
Previously, the manufacturer primarily relied on template-based (gauge) measurement. This method involved high costs for tooling design, suffered from poor precision and stability, and resulted in extremely low inspection efficiency.
The manufacturer’s product line includes two major categories—turbofan and turboprop—comprising 36 sub-types based on blade stages. This variety required inspectors to possess extensive experience for each specific type. The process was cumbersome and labor-intensive, creating an urgent need for an accurate, stable, and efficient automated method to replace manual templates.
Measurement Process
The height of the blades ranges from 30 mm to 210 mm, with a required inspection accuracy of better than 0.02 mm. The solution utilizes the AutoScan™ 500 Automated 3D Inspection System, equipped with the PowerScan® 5M Blue Light Area Scanning Sensor.

Through the acquisition of 3D measurement data, the system automatically analyzes parameters such as chord length, profile thickness, and edge radii (R-angles) across various cross-sections to determine compliance. The AutoScan™ 500 provides comprehensive and reliable quality control, accurately identifying part defects and guiding repair strategies to enhance overall production efficiency.
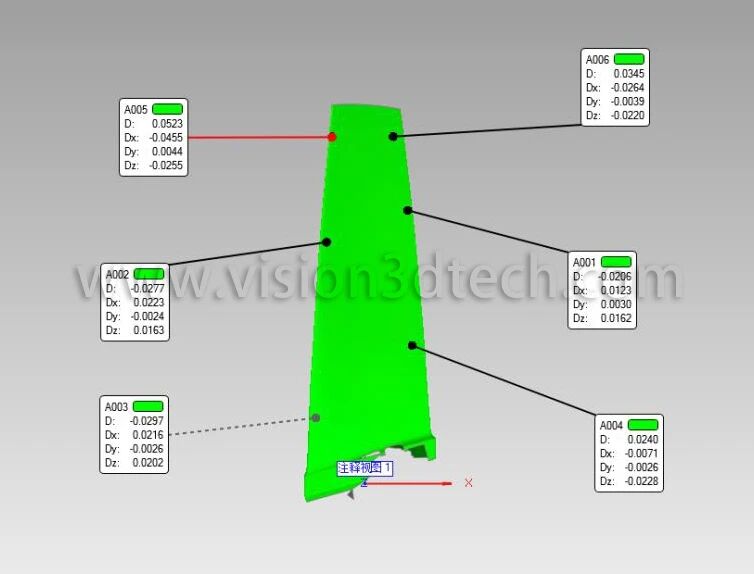
During production, the leading and trailing edges are the areas most susceptible to deformation. By monitoring the batch production process and analyzing the variation trends of these edge profiles, the system helps optimize manufacturing processes to control machining errors, thereby ensuring the quality and efficiency of thin-walled blade sections.
Case Summary
- Precision: Overall measurement accuracy ≤ 0.02 mm.
- Efficiency: Inspection time is 40 seconds per blade, achieving a throughput of 3 parts every 2 minutes.
- Capacity: Capable of completing 7,000 inspection tasks per month per station.
- Usability: One-click automated detection eliminates the need for specialized experience and minimizes human-induced error.